Hid Wiring Diagram With Relay And Anti Flicker
A typical relay power harness for HID Conversion Systems. The primary function of an automotive headlight wire harness is to provide power directly from the vehicle's battery to the lighting system. This allows the bulb, or HID ballast, to operate independently of the vehicle's original wiring system and can provide a power source that is more consistent. A lighting relay harness is most commonly used in aftermarket HID conversion kits to bypass the factory wiring in order to get around complicated electronic control systems or to allow a higher rate of current to be delivered to the bulbs. A Relay Wiring Harness utilizes a 30amp fuse protected power wire that directly connects to your positive terminal on the battery. An Automotive Relay is used to pull signal from a source (Headlight connector) that triggers power to be drawn from the battery. There are two sets of cables meant to provide power to an HID ballast. There are also two separate ground wire terminals that need to be connected to the chassis to complete the electrical circuit. The different components of the Accessory Wiring Harness. As previously stated, this product is most commonly found used in aftermarket xenon retrofits but can also be beneficial when trying to get the most light output from aftermarket or OEM halogen/incandescent light bulbs. Any lighting system can benefit from increased current capacity in the wiring. GTR Lighting offers a wide array of Plug and Play Relay Wire harnesses for H7, H8, H9, H10, H11, H13, 9004, 9005, 9006, 9007 and more. Visit GTRLighting.com to learn more about the different wiring products available. What does a Wiring Harness fix? Problem: Delayed Start Solution: Problem: Flickering Solution: Problem: Dim/Dark Light Output: Solution: Problem: Uneven Brightness Solution: To Buy or Not to Buy? Single beam relay harness diagram from GTR Lighting.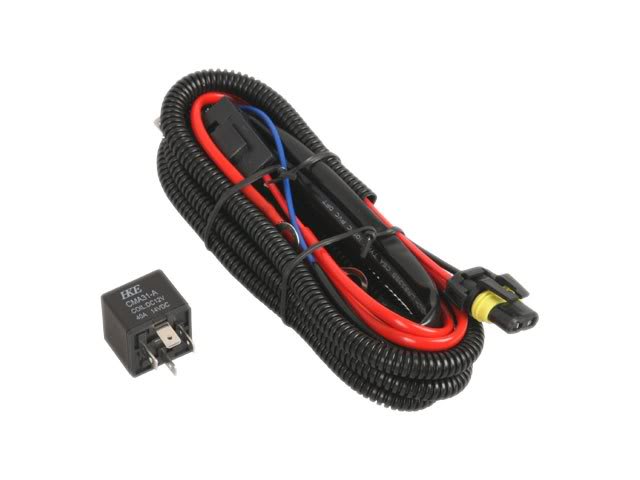 
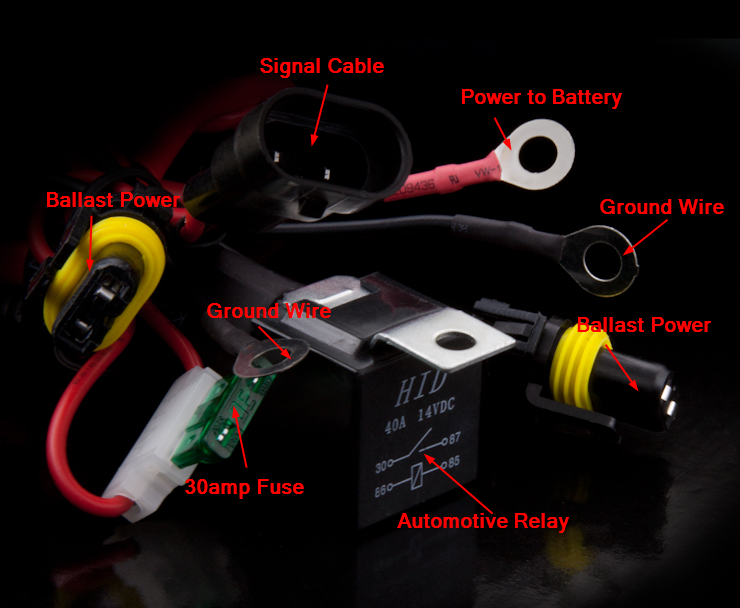
An Relay Wire Harness is capable of fixing a variety of power related HID lighting issues i.e. intermittent on/off, flickering, delayed start, HID low light output, and uneven brightness.
An HID Ballast requires more power to ignite on start-up than during normal usage. This initial power surge can sometimes be problematic for vehicles with weaker electrical systems that cannot provide the power needed. The vehicles stock headlight connectors are not capable of providing 7-8 amps per headlight and as a result, only one HID turns on when the switch is turned on. After about 20 seconds when the ballasts power consumption drops to 3.2 amps, you can quickly turn the lights off then back on and voila, both HID lights turn on. This scenario happens all the time and is the direct result of insufficient power.
An HID wiring harness with power supplied directly from the battery would eliminate this issue as it would be able to consume up to 30 amps through the batteries positive terminal to ignite both ballasts.
An HID Ballast that is not getting sufficient power from a stock headlight connector will cycle on and off as it tries to ignite and power on. This can also be a result of an inefficient ballast that is not able to convert the available power to properly ignite an HID system. I always recommend high quality HID components like the 35w CANBUS Pro ballast from GTR Lighting.
An HID wiring harness will provide the power necessary to ignite even an inefficient ballast for flicker free HID lighting.
When a ballast is under-performing, light output can appear more blue and dimmer than it should be. This is a result of the ballast not converting enough power to ignite the bulb at its optimal range. A bulb that is 4300K connected to a ballast with a weak power source, can look like an 8000K blue color with substantially lower light output.
An HID Wiring harness will be able to provide more power to the ballast allowing the system to operate at 100%. This however is not a guaranteed solution as a poor quality ballast which will not output sufficient power no matter how much is being inputted.
My passenger side is brighter than my driver side! Power in not always delivered in equal amounts to each headlight, and depending on your vehicles wiring configuration, can have a negative impact on lighting performance when installing HIDs. If one headlight has less resistance to the power source i.e. length of wiring, fuse panels bridging connections etc, it will receive power first leaving less for the second headlight to consume. In this scenario, one headlight could end up being brighter than the other, or powering up to full brightness faster than the other.
An HID wiring relay harness will provide equal amounts of power to each HID Ballast allowing for even and consistent brightness between both headlights.
An HID wiring harness for some vehicles is a safety and assurance item to prevent future problems, and for other vehicles is a necessary requirement to a successful HID installation. My general recommendation is to always use a harness where possible to help extend the life of your HID system, avoid unnecessary headaches, or to boost the output of your halogen light bulbs. Not only are you providing your HID ballasts with adequate power, you are protecting both your vehicle and HID system with the inline fuse that separates the systems.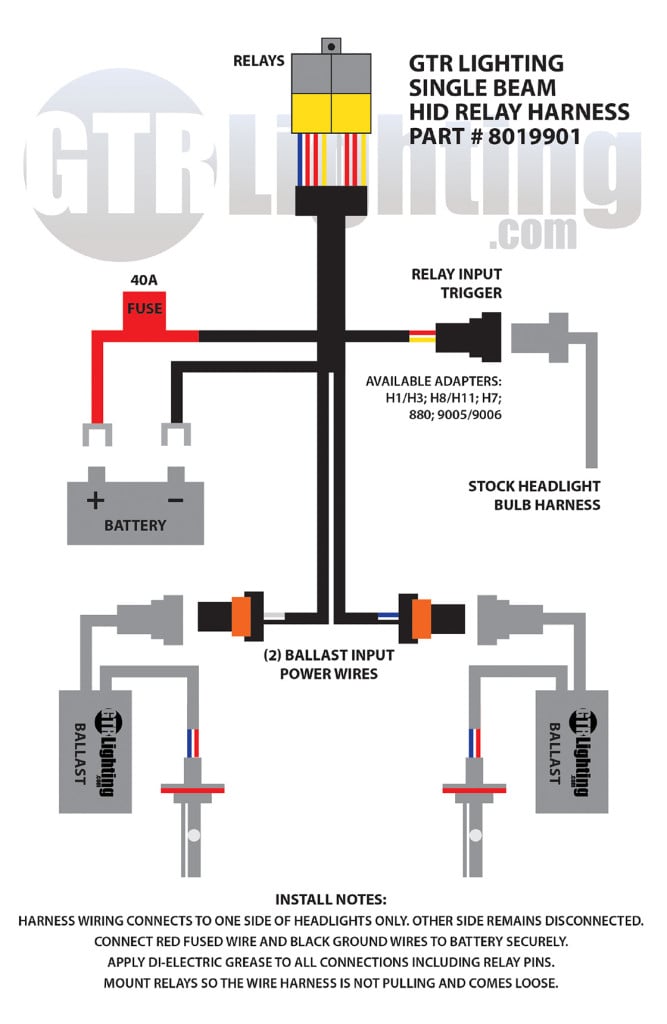
Posted by: barbarayoullifeireoau.blogspot.com
Source: https://blog.betterautomotivelighting.com/hid-relay-harnesses-explained
Posting Komentar untuk "Hid Wiring Diagram With Relay And Anti Flicker"